How To Add Nics To Device In Gns3
Actually there are several ways how to emulate JunOS routers using GNS3 and make to usable them for avant-garde networking topologies. So, exist able to brand and run JunOS inside of GNS3 nosotros could employ:
- qemu
- virtualbox
- vmware
as the toll effective variance nosotros adopt utilise open and free software, therefore nosotros are focusing on the qemu and Vitrualbox. Here once more we have several oportunities, how to prepare virtual junos router, all of them require preinstalled FreeBSD Bone. Preparing FreeBSD virtualized VM nosotros are able install a junos package than. I, as a newbie, have been tested some of mentioned opportunities. And then, offset of them, I'm using qemu.
Using qemu to run Junos router inside of GNS3
Prerequisities and environment
All components are running inside of my Win seven 64 flake OS:
- Installed GNS3. I prefer to install version for win 64 bit. Download here. I'thousand using version 0.eight.6. I'm using GNS3 version 1.2.3 at present.
- Installed Qemu, 0.11. Win 32 version in my instance. Yous can download information technology here. I'm using the one provided and installed together inside GNS3 install bundle. We need the qemu as the virtualization technology used to make and run FreeBSD VM. The FreeBSD VM is so used as the platform where nosotros install the principal JunOS.
Steps
We have to, in full general, follow the same steps:
- Create a qemu virtual machine
- Install the FreeBSD operating organisation on it (4.11).
- Install a Junos package
- the one which is preprepared. Usually named OLIVE.
- the i which we have to modify and which is based on the domestic-signed JunOS packet.
- Import the junos qemu car into GNS3 and build and run an example of topology.
Creating and installing a qemu machine with the FreeBSD OS
Equally the offset footstep we have to create a qemu virtual car. Inside of it we will install FreeBSD. The tutorial Installing FreeBSD for JunOS Olive using Qemu under Win 7 64bit is describing how to do it. For newer versions of junos OS we need to enlarge the disk size and its logical partitions. For Junos versions of 9, 10 and 11 is 4G enough, for versions 12 and higher should enlarge this up to 10G/12G.
Installing a master junos system
Now we will install a junos organization within of qemu FreeBSd virtual machine. Here over again we have several ways available, all of them require junos installation package. On the net we may establish dissimilar packages and tutorials how to practice it.
Using an olive package
We may found Junos packages which are already preprepared to run inside of FreeBSD, all running within of PC (existent or virtual). This kind of Junos packages are so called OLIVE. The olive bundle we may usually install directly inside of FreeBsD machine. The tutorial
"
Making qemu JunOS router installing JunOS 10.1 OLIVE package inside of qemu FreeBSD under Win seven 64bit
"
is describing how to practice it.
Using a domestic-signed package
Every bit the second possibility, nosotros may on the net find original Junos packages, which are preprepared to run inside of real junos HW, all are signed with hash keys. These packages have to be modified before we may install them into a qemu FreeBSD auto. Here again many tutorials are available, however in my case there are not straightforwardly applicable as I ever establish kind of installing trouble.
In general, many of them run GNS3/qemu inside of linux OS, i'm using windows, where at least ftp/scp/sftp service have to be supplied. Then we accept to alter original domestic signed junos package and make them usable for a qemu machine to install. All tutorials proposes to change the resolving of checkpic binary of the pkgtool package.
1 perfect tutorial, as "Installing Olive 12.1R1.9 under Qemu", sugest omitt the usage of signed packages (information technology remove all keys and does not making tgz package with them) and besides remove hardware platform checking. The steps described there sugest to modify 2 files (+INSTALL and +REQUIRED) and modify part of the check_arch_compatibility() function. I institute required part only within of junos packages version 10 and above, so the tutorial is not applicable for junos version ix (for instance 9.half-dozen as I had admission to).
One time I obtained a Junos package of such version I've fabricated a tutorial (march, 2015), as the usual tutorials once more did not precisely work for me. My working solution i'm describing here
"
Making a qemu JunOS router installing JunOS 12.3R6.half-dozen DOMESTIC-signed package inside of qemu FreeBSD nether Win 7 64bit
"
Some other splendid tutorial Olive reloaded or how to emulate Juniper routers describe how to modify package and generate new keys, thus making complete junos signed olive packet. Personally for older versions of Junos I have used this tutorial, but I institute there some unclear parts, especially within of backward steps used to tar a new junos olive package. My working solutions i'm describing here
"
Making qemu JunOS router installing JunOS 9.six DOMESTIC-signed package inside of qemu FreeBSD under Win 7 64bit
"
Note: Inside my tutorials I've used freebsd four.eleven and junos domestic signed packages.
Making GNS3 tolopology of juniper routers using GNS3
Version GNS3 i.x
Calculation a junos router (image)
For version GNS3 1.x open a new project. Then go to:
Edit-->Preference-->qemu--> Qemu VMs where you click on the New button
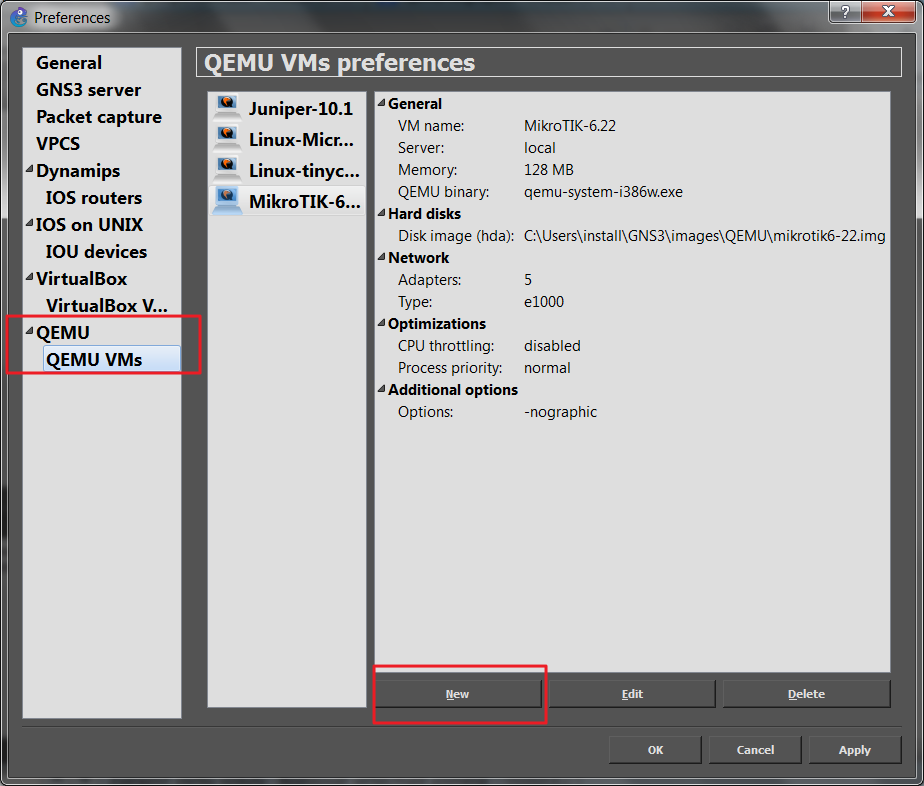
The window for adding a new Qemu machine volition open, blazon a machine name which identify your router (hither Junos-12.3R6.6)
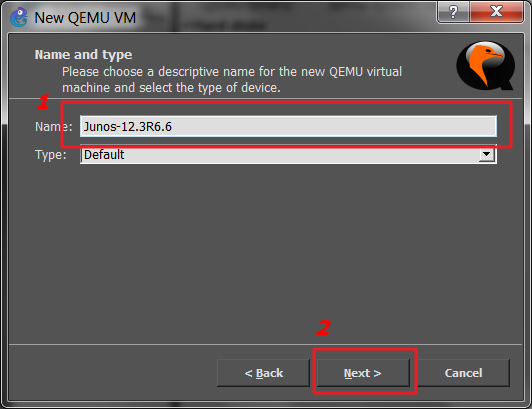
click Side by side. Then assign RAM retentiveness, here 512MB, and cheque if GNS3 locates Qemu binaries correctly. If not, open a drop down carte and choose correct Qemu binaries. Click Side by side
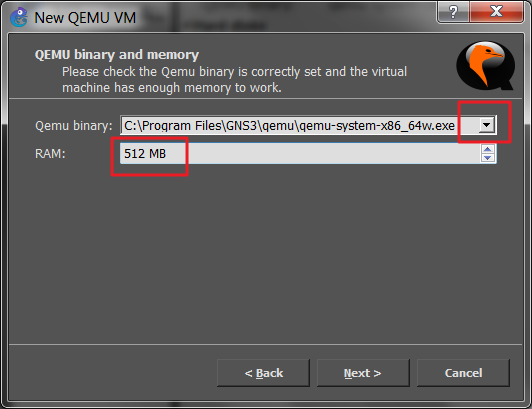
And then select right junos qemu image file (hard drive).
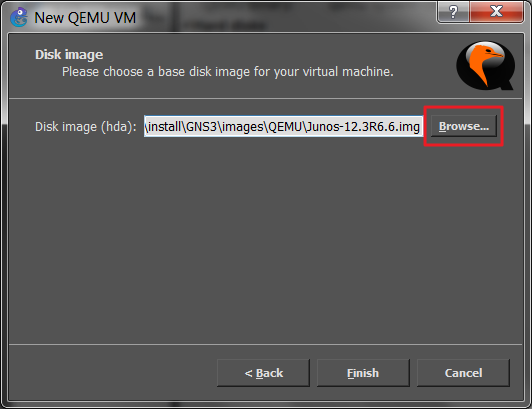
and finish adding a router clicking on the Finish push button. The router is added.
Additonaly you may select it from the list and clicking on the edit push modify the settings only we set (adding the number of adapters, -nographic options and then on.).
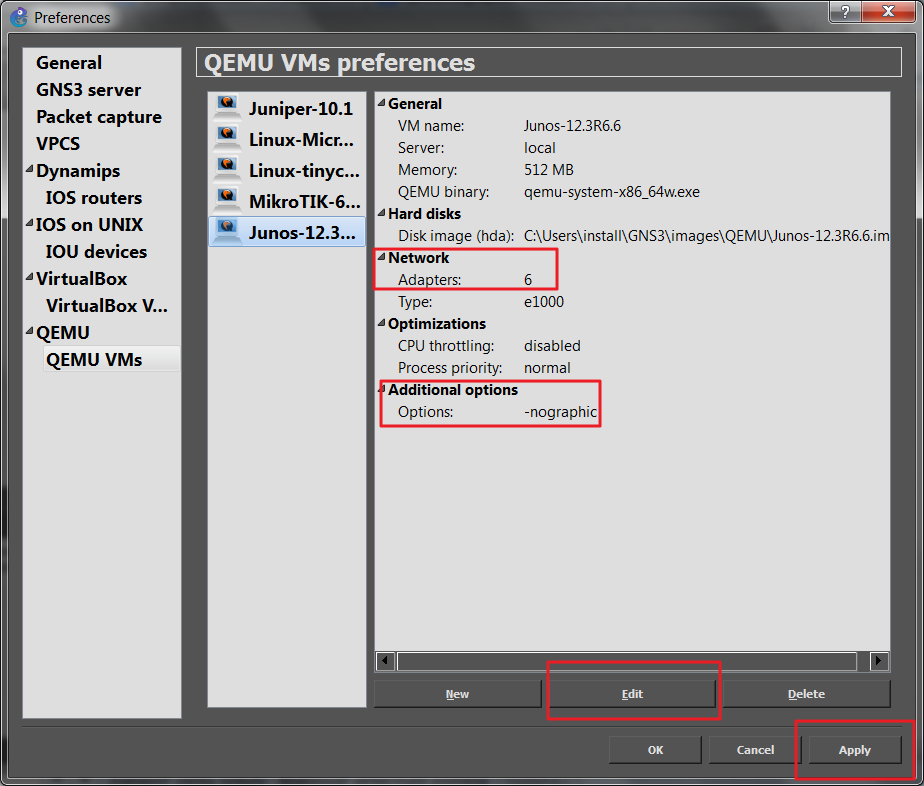
All is finished clicking on the Apply and Ok button.
Creating a topology
At present we are able drag the junos router from the left panel and drop them into working identify. Choose interconnection blazon (eth0 to eth0) and start routers as we usually do:
1) click on the Browse all devices icon (crimson number one)
2) select correct router, Junos-12.3R6.6 hither
3) drop the devices on the workspace
four) select Add link icon (4)
5) interconnect routers (5)
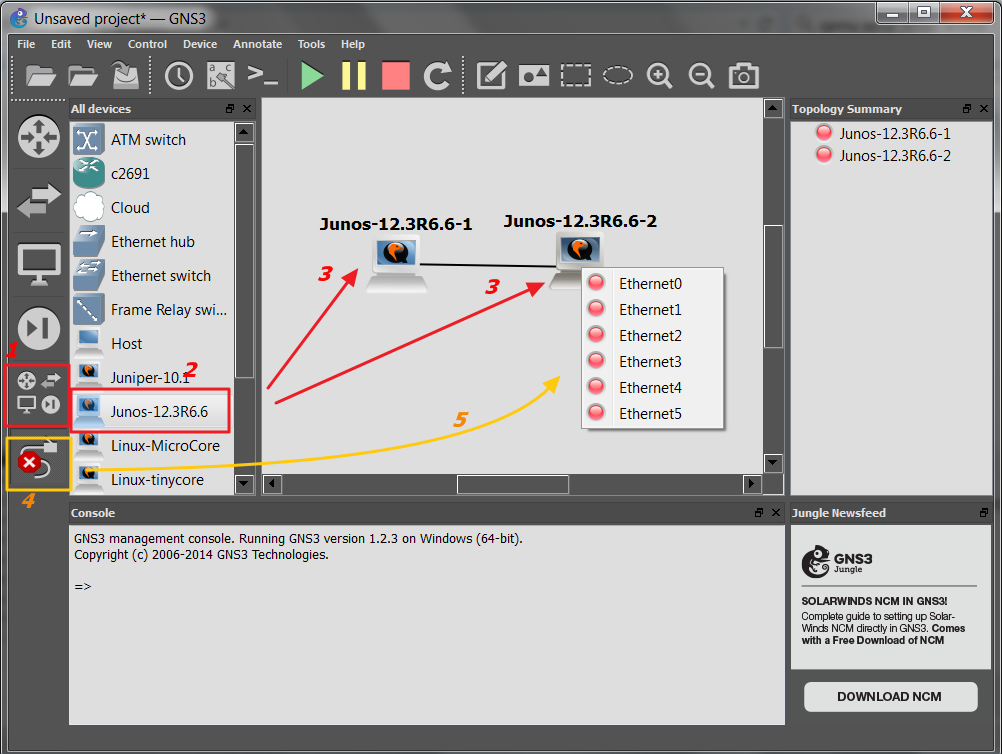
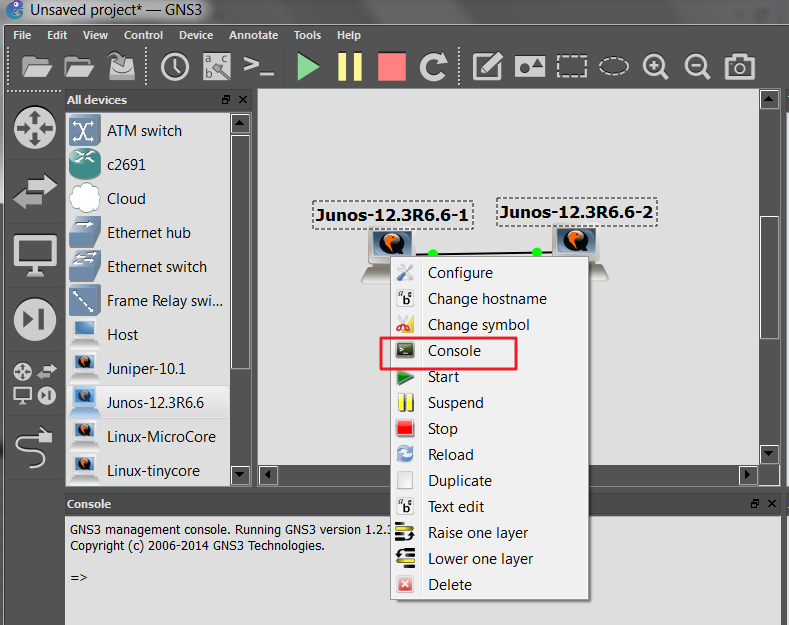
Then click on the start icon (green triangle). The router will kick up, exist patient, comparison to cisco ios it takes time. Access the router simply practice a left double click on a selected device, putty window should immediatelly appears. Or utilise a context bill of fare which is attainable afte right click on a desired router.
That is all. Now we may outset to work and learn!
Version GNS3 0.x
Following quide is for an older versions of GNS3. However even works for a newer ane, version of 1.xx
Qemu checking
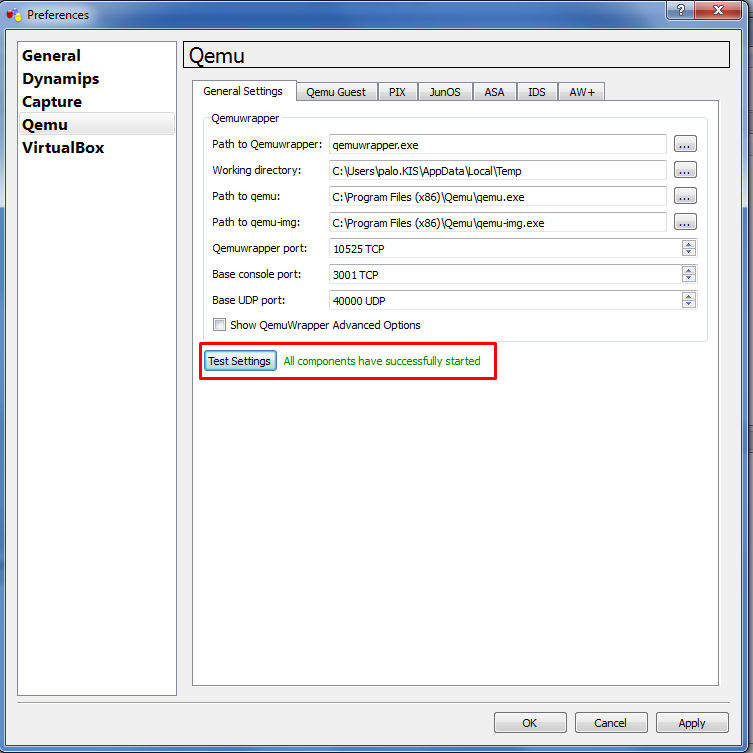
Offset of all we shoud check if our GNS3 may correctly call qemu exe files, and then go:
Edit-->Preference-->qemu--> General settings
and check if at that place are right paths to the qemu.exe and qemu-img.exe. Finally, exam the settings clicking on the Test settings button. If everything is OK, the green message should appear telling us that all components take correctly started. If at that place is some fault bulletin, correct the settings:
Adding Junos prototype
Now we may first to build a topology using our qemu build junos router running inside of our GNs3 topologies. So, first add the junos router into the qemu junos router list. To practise that go inside of GNS3 to the menu with Qemu preferences
Edit-->Preference-->quemu-->junos-->add the juniper prototype
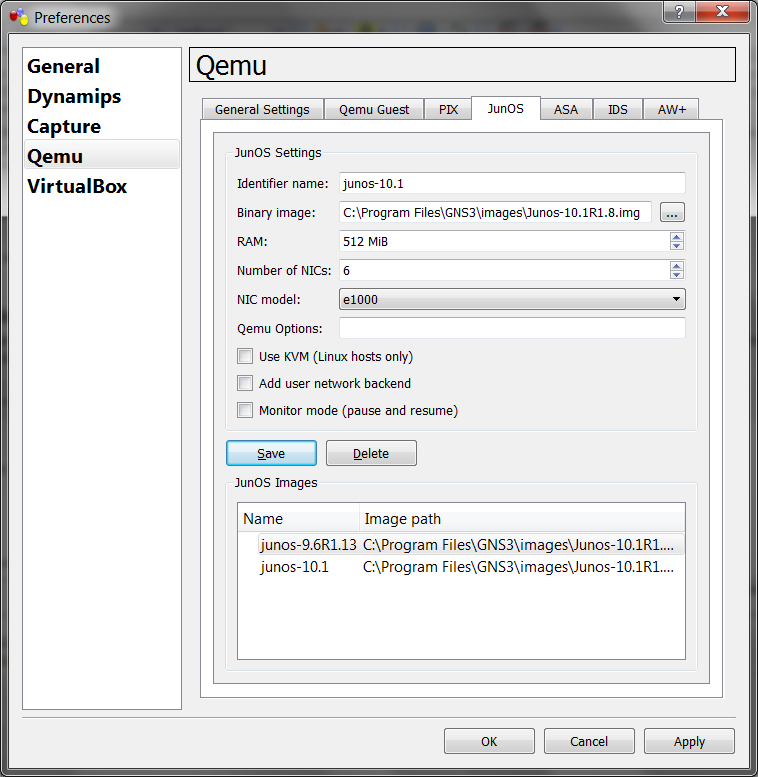
and fullfill required fileds:
Identifier name: put your router proper name (here junos),
binary image: setup correct path to the junos epitome file,
RAM: assign required menory size, may get out bare, GNS3 assign, equally in my case, 512MB
Number of NICs: default 6
NIC model: e1000
Then click Save and close the window with Utilise. At present nosotros are able elevate the junos router from the left panel and drop them into working place. Choose interconnection type (em0 to em0) and offset routers as we usually do (choose device and click on the start icon)
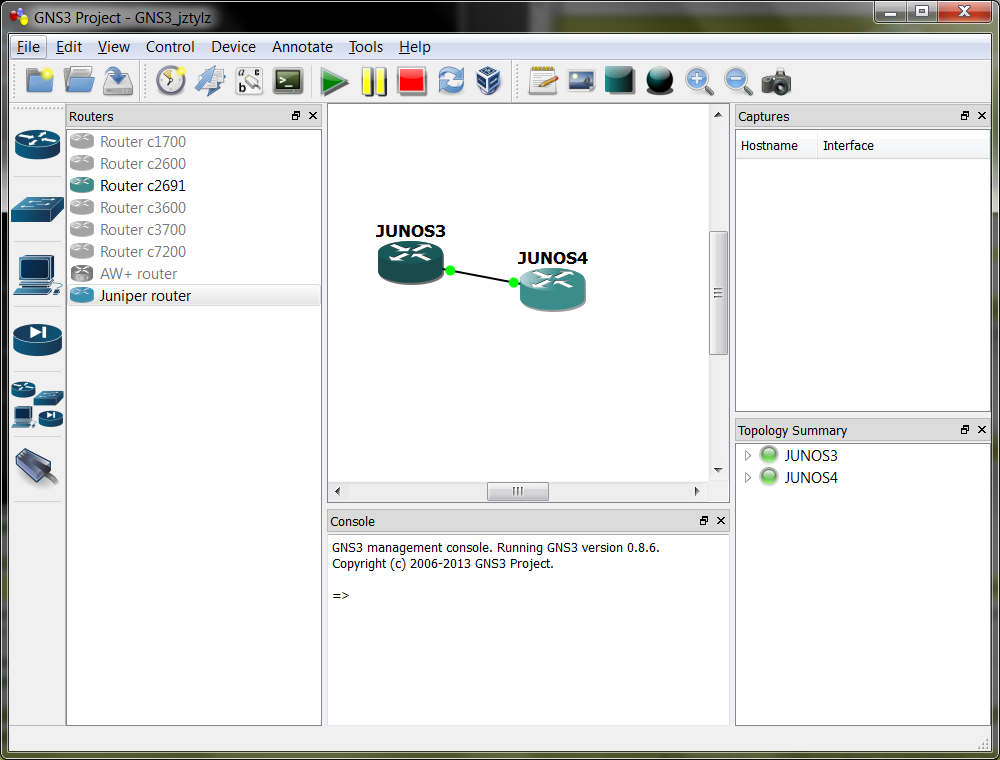
Immediatelly qemu window (-southward) will open up. At present we shoud expect for a time till the Junos router image will boot, and so the login prompt will be available:
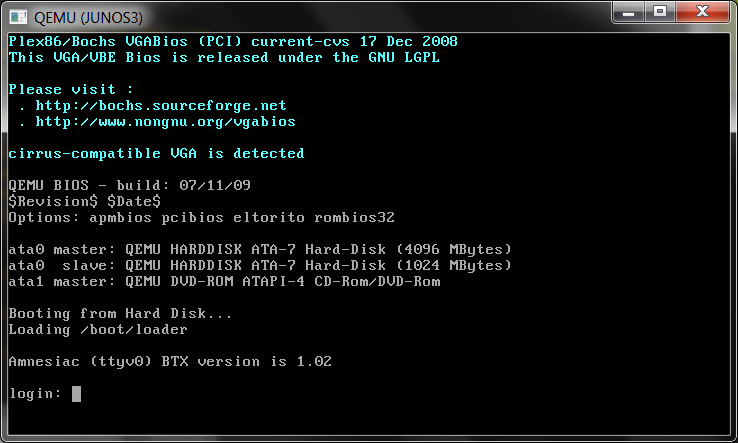
using our install login name (here root) we will log in into the junos router
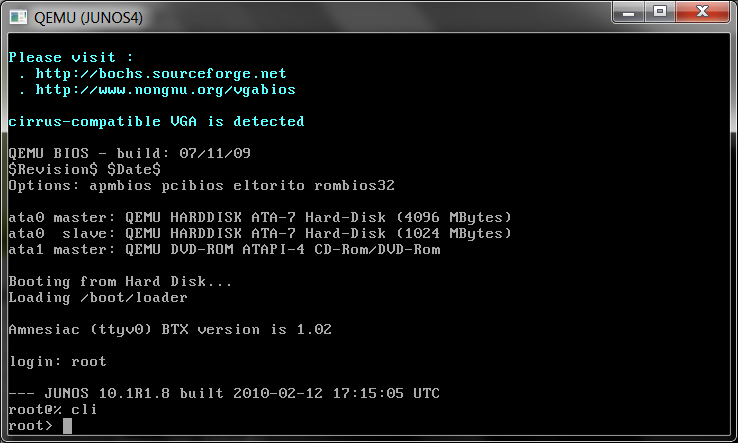
or we may observe booting and login using telnet window, so do ricght click on the device and choose console,
immediatelly window with telnet open and we may observe there booting process and at the cease, we are able to login
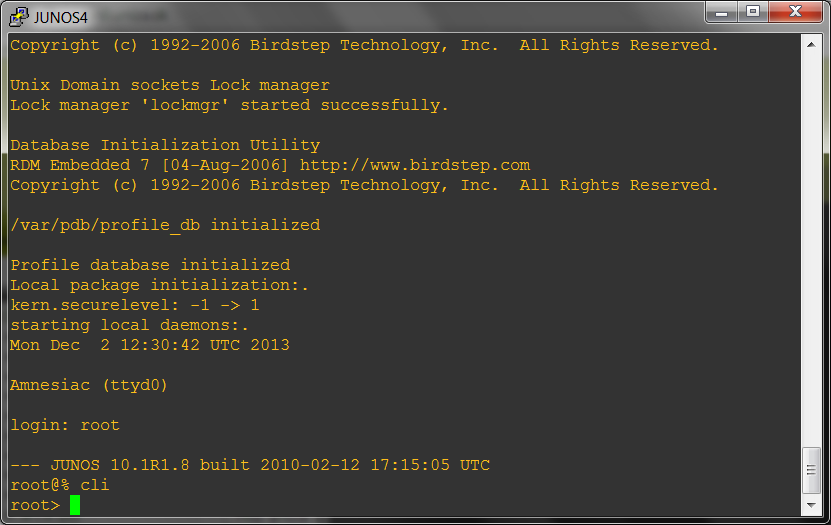
Now we may start to configure our router boxes.
Using VirtualBox to run Junos router inside of GNS3
Prerequisities and environments
- All is running inside of my Win 7 64 bit Os.
- Installed GNS3. I prefer install version for win 64 bit. Download here. I'one thousand using version 0.8.half dozen.
- Installed virtualbox, download hither.
- Some virtualbox machine with installed Junos router
How To Add Nics To Device In Gns3,
Source: https://nil.uniza.sk/how-run-junos-inside-gns3-step-step/
Posted by: tremblaytagoink.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Add Nics To Device In Gns3"
Post a Comment